 |
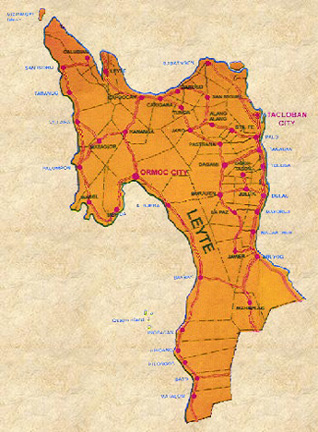
PROVINCE OF LEYTE

LOCATION
The province of Leyte is one of the six provinces of Eastern Visayas
Region in Central Philippines. Carigara Bay bound it on the north, San
Juanico Strait and Leyte Gulf in the east, Visayas Sea and Ormoc Sea in
the west, and the province of Southern Leyte in the south.
Leyte's strategic location links the two major growth centers of the
country - Manila in Luzon and Davao in Mindanao through the Maharlika
Highway. Its provincial capital is the city of Tacloban, which is one (1)
hour travel by plane to Manila, from Cebu, it is only a 30-minute travel
by plane and via the "Supercat" Ferry, which is the latest in the
state-of-the-art sea travel, Cebu is only two hours away. Thus, Leyte is
accessible by land, by sea and by air.
AREA
Leyte has an area of 5,712.8 square kilometers. About 73% of Leyte's land
resources is alienable and disposable while 27% is classified as forest
land. Its present land use is comprised of the following, namely:
irrigated rice field/fishpond - 11%; cultivated annual crops - 9%;
perennial trees vine crops - 38%; wetland forestry - 9%; pasture, shrub
and grasslands - 29%, and special land uses 2%.
Table 1. Status of Land Classification Land Classification 1985 1986-1994
Alienable and Disposable Land a/ 436,173 388,595 Total Forest Land 190,657
182,685 Unclassified Forest Land 181,750 - Classified Forest Land 8,907
182,685 Forest Reserves 1,475 15,588 Timberland b/ - 158,967 Military
Reservation - - National Parks 3,601 3,571 Civil Reservation 3,831 3,831
Fishpond Development - 728 Table 2. Land Area by Municipality Municipality
Land Area (Sq. Km.) Abuyog 344.2 Alangalang 150.5 Albuera 51.1 Babatngon
115.2 Barugo 78.5 Bato 72.4 Baybay 462.0 Burauen 264.9 Calubian 137.6
Capoocan 185.4 Carigara 114.0 Dagami 160.0 Dulag 39.0 Hilongos 192.9
Hindang 127.4 Inopacan 94.6 Isabel 63.8 Jaro 207.2 Javier 141.8 Julita
53.3 Kananga 144.2 La Paz 100.2 LeyteLeyte 147.8 MacArthur 48.6 Mahaplag
172.0 Matag-ob 75.4 Matalom 110.9 Mayorga 61.6 Merida 95.2 Ormoc City
490.5 Palo 67.6 Palompon 126.1 Pastrana 79.3 San Isidro 109.2 San Miguel
145.1 Sta. Fe 81.9 Tabango 129.2 Tabontabon 25.0 Tacloban City 101.0
Tanauan 78.4 Tolosa 22.5 Tunga 38.2 Villaba 126.0 Table 3. Status of
Irrigation System Total Arable Area Potential Irrigable Area Existing
Service Area 350,329 52,236 32,986
TOPOGRAPHY
The terrain of the province
is relatively flat to gently rolling and becoming mountainous and rough
towards the center where a mountain range begins. This cordillera divides
the province into its eastern and western plains. Peaks of approximately
2,295 to 3,280 feet high extend from north to south.
CLIMATE
The
province's eastern portion has a type II climate. It has no distinct wet
or dry season but with pronounced rainfall from November to January while
the western portion has a type IV climate with rainfall evenly distributed
throughout the year.
POPULATION
As of 1995, Leyte's population was
recorded at 1,511,251 million of whom 51% are males and 49% are females.
There are about 301,158 households at 5.5 persons per household. Its
population density is 264.54 persons per square kilometer. About 703,000
of the population belong to the labor force participation rate of 67.80%.
Its employment rate - 93.9% which 53.34 is the agriculture, 36.31% in
services and 10.22% in industry. Table 4. Total Population and Number of
Household Municipality Total Population No. of Household Abuyog 48,905
9,783 Alangalang 38,853 7,533 Albuera 33,939 6,932 Babatngon 19,653 3,789
Barugo 26,171 4,826 Bato 29,810 5,898 Baybay 86,179 17,579 Calubian 31,074
6,403 Capoocan 26,384 5,324 Carigara 42,302 8,524 Dagami 27,039 5,500
Dulag 34,742 7,012 Hilongos 50,744 10,062 Hindang 16,567 3,506 Inopacan
18,864 3,748 Jaro 32,726 6,644 Javier 21,539 4,214 Julita 11,671 2,433
Kananga 39,795 7,783 La paz 16,366 3,264 Leyte 34,126 6,411 Macarthur
16,645 3,139 Mahaplag 24,009 4,613 Matalom 28,232 Matag-ob 17,333 3,512
Mayorga 11,073 2,288 Merida 23,822 5,372 Ormoc City 144,003 29,391 Palo
43,095 8,345 Palompon 50,319 10,789 Pastrana 14,442 San Isidro 33,204
7,098 San Miguel 14,504 2,779 Sta. Fe 13,695 2,665 Tabango 31,837 6,385
Tabontabon 7,547 1,547 Tacloban City (Capital) 167,310 30,851 Tanauan
40,716 8,315 Tolosa 13,927 2,839 Tunga 6,530 1,055 Villaba 34,674 7,113
POLITICAL/ADMINISTRATIVE SUB-DIVISIONS
The province of Leyte is composed
of two cities - Tacloban and Ormoc, 41 municipalities and 1,641 barangays.
Table 5. List of Municipalities and Barangays City/Municipality Number of
Barangays Abuyog 13 Alangalang 54 Albuera 16 Babatngon 25 Barugo 37 Bato
32 Baybay 92 Burauen 77 Calubian 53 Capoocan 21 Carigara 49 Dagami 65
Dulag 45 Hilongos 51 Hindang 20 Inopacan 20 Isabel 24 Jaro 46 Javier 28
Julita 26 Kananga 23 La Paz 35 Leyte 30 MacArthur 31 Mahaplag 28 Matag-ob
21 Matalom 30 Mayorga 16 Merida 22 Ormoc City 110 Palo 33 Palompon 50
Pastrana 29 San Isidro 19 San Miguel 21 Sta. Fe 20 Tabango 13 Tabontabon
16 Tacloban City 138 Tanauan 54 Tolosa 15 Tunga 8 Villaba 35
ROADS AND
BRIDGES
Leyte's roads are generally of concrete-cemented conditions with a
total road length of 3,157.537 kilometers. The main artery is 830 kms. Of
national roads, interconnected with 473.651 kms. Of provincial roads,
326.782 kms. of municipal roads. Along the road system are bridges
totaling 12,153.450 meters of which 10,596 meters are national and
1,557.450 meters are provincial bridges.
AIRPORTS
The DZR Airport in
Tacloban City is the trunkline of the airports of Leyte. Secondary
airports are located in Ormoc City and Hilongos, Leyte. The DZR Airport
accommodates Boeing 737 aircraft with its total runway of 2,400 kms. and
an open terminal area of 19,150 sq. m.. The Philippine Airlines, Grand
Air, Cebu Pacific Air and the latest addition was Asian Spirit provide
regular flights to/from Manila and Cebu. Other air trips are two feeder
airports owned by Philphos and PNOC at the Leyte Industrial Development
Estate in Isabel, Leyte.
SEAPORTS
The province has 24 seaports - two of
which are considered national ports, which are located in the cities of Tacloban and Ormoc. All other main ports are located in Isabel, Palompon,
Bato, Baybay and Hilongos. The Tacloban Port is the center-shipping harbor
in Eastern Visayas. Inter-island ships ply the Tacloban-Cebu--Tacloban and
the Tacloban-Manila-Tacloban routes.
WATER SUPPLY
The Leyte Metropolitan
Water district (LMWD) supplies water to Tacloban City and nearby
municipalities. The P200 million water treatment rehabilitation project of
the LMWD has recently been completed thus improving the supply of water in
the entire province.
POWER
The Tongonan Geothermal Power Plant of the
National Power Corporation (NPC) supplies the power requirements of the
province. It has a generating capacity of 112.5 MW of which 93.93 MW are
used in the whole region and the LIDE in Isabel. Excess power ready for
use is therefore 18.57 MW. NPC now offers direct connection to industries
that consume 2,000 kilowatts and higher. Preferential rates from the local
cooperatives are negotiable for industry located in their respective areas
of operation.
COMMUNICATIONS
State-of-the-art communications facilities
are in place. EVTELCO, based in Tacloban City, has six telephone exchanges
that offer direct dial services for domestic and overseas call. PLDT, RCPI,
PT & T and Concha Radio Network also serve the communication needs of the
province. All 41 municipalities have telegraph stations. Mobiline, Piltel,
Smart and Islacom cellular phone companies, is catering cellular phone
services. Internet already links the province to the world via two
Internet servers operating in Tacloban City.
TOURISM
Leyte is a showcase
of rich history and culture set in an unspoiled environment of natural
beauty and rustic elegance. The provincial government has started
organizing cultural festivals in the province for tourism promotion.
Notwithstanding, historical sites abound in Leyte. In almost all its town,
relics of houses, monuments, churches and other structures dating back to
the Spanish colonial era could still be found.
MAJOR EXPORT
PRODUCTS/RESOURCES
As to Leyte's resources, rice, coconut, sugarcane are
the main agricultural products. Existing major Agri-based industries are
copra oil exported to Korea, U.S.A., and the People's Republic of China;
raw and refined sugar exported to the U.S.A., and Japan. Leyte has also
vast marine shipping grounds along some 29 coastal municipalities.
Existing aqua-marine-based industries are prawn culture for export to
Japan. Metallic and non-metallic mineral resources are also abundant in
the province. Among which are copper, manganese, rock phosphate, peat,
bentonic, dolomite and rock asphalt. Leyte houses the largest phosphatic
fertilizer plant in Asia and one of the biggest copper smelters in the
world. Philippine exports of copper cathodes, concentrates and ores
primarily came from the province of Leyte since the Philippines' only
copper smelting plant is located in Leyte. Leyte forest yield indigenous
raw material used in industrial production such as rattan, bamboo, buri,
nito, wild vines and ferns. In recent years, there has been some growth in
small-scale industries engaged in the manufacturers of gift items, toys
and housewares utilizing these raw materials.
INDUSTRIAL GROWTH CENTER
The
province occupies a very critical position to the over-all economic
development of Eastern Visayas. Availability of prime land for developers
and investors is evidenced by the establishment/operationalization of the
following growth center namely; · The Leyte Industrial Development Estate
in Isabel, Leyte · The Eastern Visayas Agro-Industrial Growth Center in
Tacloban City · The San Isidro Eco-Tourism Zone houses the Amihan Cebu
Woodlands Township Project in San Isidro · The Leyte Special Eco-Tourism
Zone in Palo, Leyte · The Barugo Eco-Tourism Zone in Barugo, Leyte · The
Leyte Integrated Resource Management Center in Sta. Fe, Leyte · The Baybay
Techno-Science Park in Baybay, Leyte.
BRIEF HISTORY
The "discovery" of
the Philippines took place on March 28, 1521, the day Ferdinand Magellan,
a Portuguese navigator in the service of the Spanish crown, landed in Limasawa, a 5-square mile island at the southern tip of Leyte mainland.
Here Magellan met the native ruler, Rajah Kulambu, and his brother Rajah
Siago, chieftain of Butu (in Mindanao). In this little island, the first
recorded blood compact or treaty of friendship between Magellan and Rajah
Kulambu took place. The first mass was celebrated, and Magellan, after
planting a cross on a hilltop, took possession of the territory in the
name of Spain. In 1595, the Jesuits established the first mission in Leyte.
At this time, there were only 19 pueblos with 70,000 people whom the
missionaries converted to Christianity, easing the settlement of the
province by Spanish conquestadores. The Jesuit mission was abandoned when
the Order was expelled from the Philippines in 1768. Politically, Leyte
seems to have existed as early as 1622. The simple structure of government
by encomenderos gave way to alcalde mayores, corregidores and tenientes.
In 1735, Leyte was a politico-military province with jurisdiction over
Samar. The two provinces were politically separated in 1768 by royal
Decree of July 31, 1860 which ordered the reorganization of provincial
governments of the Visayas.
Leyte was classified as a third class
province; it had then 28 pueblos or villages. The politico-military
government existed until the end of the Spanish rule in the Philippines.
The capital site of Leyte changed several times before Tacloban City
became the permanent capital in 1787. The first capital was Carigara, then
successively Palo and Tanauan. Leyte today is designated as the regional
capital of Region VIII, under the integrated reorganization plan.
Table 6.
Agricultural Commodity Situationer (CY July, 97- June 1998) COMMODITY (1)
AVAILABLE SUPPLY (MT) (2) CONSUMPTION (MT) (3) SUFFICIENCY LEVEL %
(2)/(3)=(4) RICE 98,339.5 145,494.6 67.6 WHITE CORN 3,313.71 (GRITS)
50,342.3 7.05 VEGETABLES (Fruit & Yellow) 4,114.25 50.454.15 8.15 (Green
Leafy) 965.08 11,834.92 8.15 PORK 6,001.71 13,154.80 45.62 BEEF 1,886.10
2,121.17 88.92 CARABEEF 2,698.84 3,796.72 71.08 Chicken Meat 2,728.78
9,738.13 28.02 Chicken Eggs 644.74 6,387.64 10.09
DA - RFU 8 CONTRIBUTION
TO LEYTE'S AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN 1997 DEVELOPMENT FOCUS/ SPECIFIC
MICRO- LOCATION COST AREA CONCERN PROJECT (Php.)
A. Gintong Ani for Grains
1. Production Support * Establishment of 30 Rice Palo, Sta. Fe, 70,000
Technology Demonstration Pastrana, Tanauan, Project Jaro, Burauen, Dulag,
Macarthur, Capoocan, and Hindang ( 3 sites Per municipality). 2.
Irrigation Infra Support * Construction of Small District 1 - 3 units
40,000 Farm Reservoir (SFR) District 3 - 5 units *
Distribution/installation of District 1 - 1 unit 240,000 Shallow Tube Well
(STW) District 2 - 4 units District 4 - 1 unit * Diversion Dam (DD)
District 3 - 2 units 600,000 * Small Water Impounding District 1 - 1 unit
2,250,000 Project (SWIP) 3. Post-Harvest Techno- * Construction of Multi-
District 1 - 5 units 2,820,000 logy Development Purpose Drying Pavement
District 2 - 18 units (MPDP) District 3 - 5 units District 4 - 4 units
District 5 - 15 units B. Gintong Ani for Livestock 1. Production Support *
Establishment of Animal Javier, Carigara, 140,000 Techno-Demo Anchor
Alang-alang and Farm Module San Miguel * Animal Health Services
Province-wide 100,000 2. Animal Production * Barangay Livestock (Credit
Assistance) Breeding Loan Program (BLBLP) - Cattle (11 head per Merida,
Matag-ob, 1,200,000 packet) Albuera, Kananga, Palompon and Isabel. - Goat
( 21 head per Tacloban, Alang2, 378,000 packet) Palompon, Tunga, Carigara,
Dagami And Leyte,leyte C. Gintong Ani for Fisheries 1. Production Support
* Establishment of Techno- Demo - Grouper Fish Cage Tabango and 50,000
Palompon - Seaweed Tabango and San 50,000 Isidro - Green Mussel Culture
Baybay 20,000 (Tahong) * Establishment Seaweed Canigao Island, 50,000
Nursery Matalom * Establishment of Fish Plaridel, Baybay Sanctuary Total
8,008,000
 |



![]()